Prefabricated Homes – Affordable and Efficient Housing Options with Fast Installation
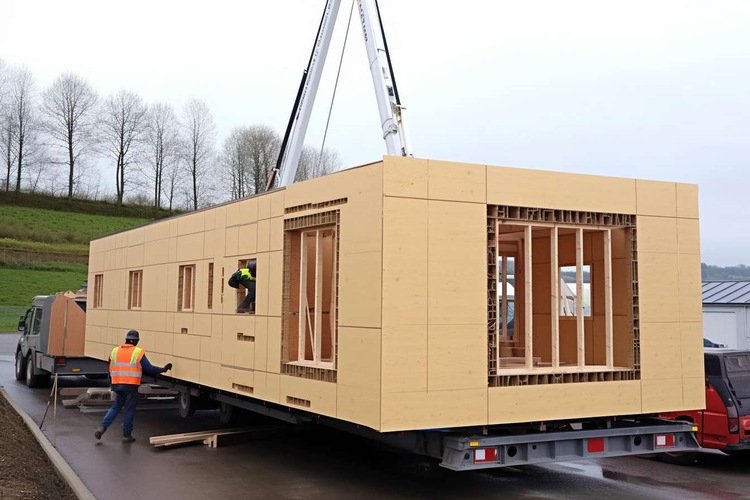
Prefabricated homes represent a revolutionary approach to residential construction, offering homeowners a faster, more cost-effective alternative to traditional building methods. These factory-built structures combine quality craftsmanship with streamlined production processes, delivering complete housing solutions that can be assembled on-site in a fraction of the time required for conventional construction.

Prefabricated Homes – Affordable and Efficient Housing Options with Fast Installation
Choosing a home-building method is no longer limited to fully on-site construction. Prefabricated homes shift much of the work into a factory setting, then bring major components to your property for installation. That change can affect timelines, inspections, budgeting, and even how you plan site access for delivery and cranes.
What are prefabricated homes and how do they work?
Prefabricated homes are residences built partially or mostly off-site, then transported and assembled on a prepared foundation. The typical workflow includes selecting a plan, engineering it for the specific site and local requirements, factory fabrication, transportation, and on-site set and finish work (joining sections, weatherproofing seams, and completing utility connections). Because major steps happen indoors, materials are usually less exposed to rain, snow, and prolonged humidity during framing and enclosure.
How do efficient prefabricated homes compare to traditional construction?
Efficiency often comes from shorter on-site schedules and more predictable sequencing. Factory production can support consistent quality control, but the final outcome still depends on foundation accuracy, installation workmanship, and finishing trades. Energy performance is not automatic; it depends on insulation levels, air sealing, window quality, and careful detailing at connection points where modules or panels meet. Traditional construction can match these results, but it usually requires stronger on-site coordination to reduce rework, weather-related delays, and variability between crews.
What types of prefabricated home designs are available?
Prefab is an umbrella term with several build methods and design styles. Modular homes arrive as 3D modules that are set on a foundation, often allowing a faster path to a weather-tight structure once delivered. Panelized homes ship as wall, roof, and floor panels, which can reduce shipping volume and offer flexibility, but may involve more on-site labor than modular. Manufactured homes are built on a chassis under the federal HUD Code and are typically delivered in sections; placement rules, foundations, and financing can differ from modular homes built to state or local codes. Across these categories, designs range from compact ADU-style units and ranch layouts to larger two-story floorplans, with customization varying by provider and region.
Understanding prefabricated home costs and providers
Real-world budgets typically include more than the advertised “home price.” Key drivers include square footage, rooflines, window and door packages, kitchen and bath specifications, and energy-efficiency options. Many projects also have significant site-dependent costs that vary across the United States: grading and drainage, foundation type, utility trenching and hookups, driveway or access improvements for large deliveries, crane time, and permitting and inspection fees. Transportation distance and route constraints (bridge limits, overhead wires, narrow roads) can also influence total cost.
Below is a fact-based overview of established U.S. providers commonly associated with manufactured, modular, or prefab-style housing. The cost figures are broad estimates because final pricing depends on location, finishes, project scope, and site work, and some providers sell through regional plants or retailer networks.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Manufactured and modular homes (varies by model/region) | Clayton Homes | Many manufactured models are often advertised starting around $60,000–$120,000+; modular home packages commonly price higher depending on specs and region |
| Modular homes (brand varies by market) | Champion Homes | Modular packages are frequently estimated around $120–$250+ per sq ft before site work, depending on design and finish level |
| Modular homes (regional brands and plants) | Skyline Champion | Often estimated in a similar range, roughly $120–$250+ per sq ft for modular packages, excluding site work |
| Manufactured and modular homes (regional offerings) | Cavco Industries (Cavco Homes) | Manufactured homes are often seen starting around $70,000–$130,000+ depending on size and options; modular typically higher with customization |
| Prefab-style home packages (scope varies) | Deltec Homes | Design-forward prefab packages are often estimated around $200–$400+ per sq ft depending on options and build scope |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
How do zoning laws and building codes affect prefab installation?
Zoning and codes determine what you can place on a specific parcel and what the structure must include to pass inspections. Zoning rules address land use and placement, including setbacks, minimum dwelling size, height limits, allowable ADUs, and sometimes exterior design standards. Building codes address safety and performance, such as structural loads for wind, snow, and seismic conditions, fire protection, and energy requirements. In many areas, modular homes are built to the same state and local building codes as site-built homes, with inspections occurring both in the factory and on-site; manufactured homes follow the federal HUD Code, with local requirements still affecting foundations, tie-downs, and utility connections.
Prefabricated homes can be a practical option when you evaluate the full project scope: factory build method, installation logistics, site work, and the regulatory pathway. Comparing prefab and traditional construction on equal terms—timeline, performance targets, and total installed cost—helps clarify which approach fits your property and long-term housing goals.